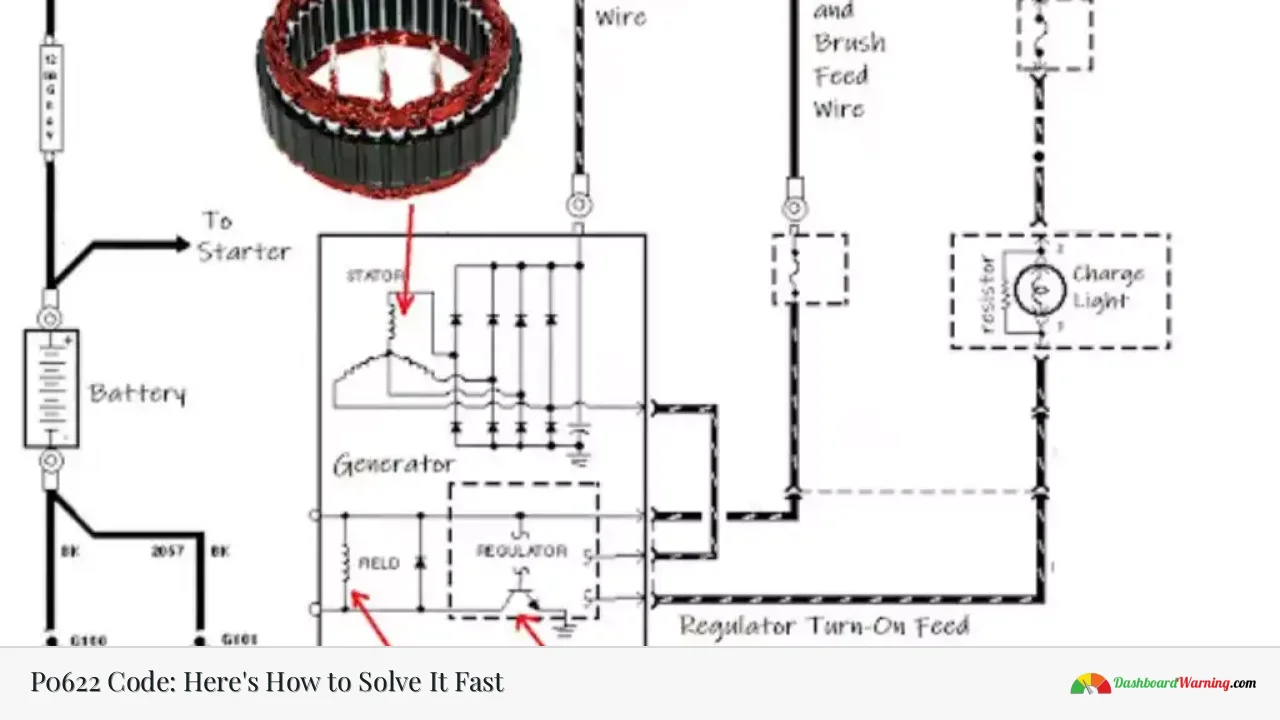
The P0622 trouble code is a generic powertrain code related to the vehicle's charging system. It specifically indicates a malfunction in the generator field control circuit, also known as the "F" terminal circuit. This code is set when the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) detects an issue with the signal from the alternator's field coil control circuit, which is crucial for proper alternator function and battery charging.
| P0622 Code Meaning | P0622 Code Common Causes |
|---|---|
| Generator Field/F Terminal Circuit Malfunction | Faulty alternator |
| PCM-detected issue in alternator field control | Damaged wiring or connectors |
| Charging system performance problem | Defective voltage regulator |
| Alternator field coil circuit continuity or voltage issue | Faulty PCM |
| Generator output signal abnormality | Corroded or loose battery terminals |
Faulty Alternator
A faulty alternator is one of the most common causes of the P0622 code. The alternator is responsible for charging the battery and powering the electrical systems while the engine is running.
Symptoms:
- Dimming or flickering lights
- Battery warning light on the dashboard
- Difficulty starting the vehicle
- Strange noises coming from the alternator
- Electrical system failures
Technical explanation:
The alternator contains a rotor with an electromagnetic field coil. When the engine runs, the rotor spins inside a stator, generating electricity. If the alternator fails, it can't produce the required voltage, leading to a P0622 code.
Step-by-step diagnosis:
- Visually inspect the alternator for signs of damage or wear.
- Check the alternator belt for proper tension and condition.
- Use a multimeter to test the alternator's output voltage with the engine running.
- Perform a load test on the alternator to check its performance under stress.
- Inspect the alternator's internal components if possible.
Solution methods:
- Replace the faulty alternator with a new or remanufactured unit.
- If the alternator is relatively new, it may be covered under warranty.
- In some cases, rebuilding the alternator might be a cost-effective option.
Cost estimates:
- Alternator replacement: $200 to $600, depending on the vehicle make and model.
- Alternator rebuild: $100 to $250, if available.
Warning: Always disconnect the battery before working on the alternator to avoid electrical shock or damage to the vehicle's systems.
Damaged Wiring or Connectors
Wiring issues can cause intermittent or constant problems with the generator field control circuit, triggering the P0622 code.
Symptoms:
- Intermittent charging system failures
- Corrosion on battery terminals or alternator connections
- Visible damage to wiring harnesses
- Burning smell from the engine bay
Technical explanation:
The generator field control circuit requires proper continuity and insulation to function correctly. Damaged wires can cause short circuits, open circuits, or high resistance, all of which can trigger the P0622 code.
Step-by-step diagnosis:
- Visually inspect all wiring and connectors related to the alternator and battery.
- Check for signs of chafing, melting, or rodent damage on the wires.
- Use a multimeter to test continuity in the generator field control circuit.
- Perform a voltage drop test across connections to identify high-resistance points.
- Inspect the alternator plug and PCM connectors for corrosion or loose pins.
Solution methods:
- Repair or replace damaged wiring sections.
- Clean corroded connections and apply dielectric grease.
- Replace faulty connectors or terminals.
- Use heat shrink tubing to protect repaired wires.
Cost estimates:
- DIY wire repair: $20 to $50 for materials.
- Professional wiring repair: $100 to $300, depending on the extent of damage.
Recommendation: Always use the correct gauge wire and proper crimping tools when repairing automotive wiring to ensure a reliable connection.
Defective Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator controls the alternator's output to maintain a consistent charging voltage. A faulty regulator can cause charging issues and trigger the P0622 code.
Symptoms:
- Overcharging (battery boiling)
- Undercharging (weak battery)
- Fluctuating voltmeter readings
- Electrical system malfunctions
Technical explanation:
Modern voltage regulators are often integrated into the alternator or controlled by the PCM. They adjust the field current to maintain the correct charging voltage, typically around 14.2 volts. A defective regulator can cause voltage fluctuations or incorrect charging levels.
Step-by-step diagnosis:
- Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage with the engine off and running.
- Monitor the charging voltage at different engine speeds.
- Perform a load test to check voltage regulation under varying conditions.
- Inspect the voltage regulator for physical damage if externally mounted.
- Use a scan tool to check for any communication issues between the PCM and regulator.
Solution methods:
- Replace the voltage regulator if it's a separate component.
- If integrated into the alternator, replace the entire alternator assembly.
- Update PCM software if available, as some regulation issues can be software-related.
Cost estimates:
- External voltage regulator replacement: $50 to $200.
- Alternator replacement (with integrated regulator): $200 to $600.
Warning: Overcharging can damage the battery and other electrical components. If you suspect a voltage regulator issue, address it promptly to prevent further damage.
Faulty Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
While less common, a faulty PCM can cause communication issues with the alternator, leading to a P0622 code.
Symptoms:
- Multiple electrical and engine management issues
- Inconsistent alternator performance
- Check Engine Light stays on after other repairs
- Vehicle fails to start or stalls unexpectedly
Technical explanation:
The PCM controls various aspects of the vehicle's operation, including alternator output in many modern vehicles. If the PCM is faulty, it may misinterpret signals from the alternator or fail to properly control the charging system.
Step-by-step diagnosis:
- Perform a full system scan to check for additional trouble codes.
- Verify that all other charging system components are functioning correctly.
- Check for any technical service bulletins (TSBs) related to PCM issues for your vehicle model.
- Test the PCM's ability to communicate with a scan tool.
- Perform a voltage drop test on the PCM's power and ground connections.
Solution methods:
- Update the PCM software if available.
- Repair any damaged connections to the PCM.
- Replace the PCM if determined to be faulty.
- Reprogram the new PCM to match your vehicle's specifications.
Cost estimates:
- PCM software update: $50 to $200.
- PCM replacement and programming: $500 to $2000, depending on the vehicle make and model.
Recommendation: PCM replacement should be considered a last resort after all other potential causes have been ruled out. Always ensure the new PCM is correctly programmed for your specific vehicle.
Corroded or Loose Battery Terminals
Poor battery connections can mimic alternator problems and trigger the P0622 code by causing voltage fluctuations in the charging system.
Symptoms:
- Difficulty starting the vehicle
- Intermittent electrical issues
- Visible corrosion on battery terminals
- Loose or damaged battery cables
Technical explanation:
The battery serves as a buffer in the electrical system. Poor connections can cause voltage drops and spikes, which may be interpreted by the PCM as a generator field control circuit issue.
Step-by-step diagnosis:
- Visually inspect the battery terminals for corrosion or looseness.
- Check the battery cable ends for fraying or damage.
- Perform a voltage drop test across the battery connections.
- Test the battery's state of charge and capacity.
- Inspect the battery tray and hold-down for any issues that could cause movement.
Solution methods:
- Clean the battery terminals and cable ends with a wire brush.
- Apply a protective coating to prevent future corrosion.
- Replace damaged battery cables or terminals.
- Ensure the battery is securely mounted in the vehicle.
Cost estimates:
- DIY battery terminal cleaning and protection: $10 to $30.
- Professional battery service: $50 to $100.
- Battery cable replacement: $50 to $200, depending on the vehicle.
Warning: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal first and reconnect it last to avoid short circuits when working on battery connections.
In conclusion, the P0622 code, while often related to alternator issues, can have multiple causes within the charging system. Proper diagnosis is crucial to avoid unnecessary parts replacement and ensure a lasting repair. If you're uncomfortable with electrical diagnostics or lack the necessary tools, it's best to consult a professional mechanic. Remember that solving electrical issues often requires patience and methodical troubleshooting.
Frequently Asked Questions About P0622
- Can I drive my car with a P0622 code?
While possible, it's not recommended. The charging system may fail, leaving you stranded or causing further damage. - How urgent is it to fix a P0622 code?
It's relatively urgent. Ignoring it can lead to battery failure, electrical system damage, or being stranded. - Will a P0622 code clear itself?
Typically, no. The underlying issue needs to be resolved before the code will clear permanently. - Can a bad battery cause a P0622 code?
Yes, indirectly. A weak battery can cause the charging system to work harder, potentially triggering the code. - How long does it take to diagnose and fix a P0622 code?
Diagnosis usually takes 1-2 hours. Repair time varies from 30 minutes for simple fixes to several hours for complex issues. - Is it safe to replace the alternator myself?
If you have mechanical experience, yes. However, be cautious of electrical connections and belt tension. - Can weather conditions trigger a P0622 code?
Extreme temperatures can stress the charging system, potentially triggering the code if components are marginal. - How often should I have my charging system checked?
It's recommended to have your charging system inspected annually or if you notice any electrical issues.
Was this page helpful?

More important content about Engine Codes
P2419 Code: Here's How to Solve It Fast
P0090 Code: Here's How to Solve It Fast
P1717 Code: Here's How to Solve It Fast
P0313 Code: Here's How to Solve It Fast
P1405 Code: Here's How to Solve It Fast
Tips and Advice
Porsche Cayenne Years To Avoid
Subaru Legacy Years To Avoid - 5 Worst Years
Pt Cruiser Years To Avoid
Use 5w30 instead of 0w20 - Advantages and Disadvantages
Tractor Dashboard Symbols And Meanings
Suzuki Sx4 Years To Avoid - 5 Worst Years